TCT 2018, Day Three: Intravascular Imaging and Anticoagulation
Today’s late breakers included studies of IVUS, near infrared spectroscopy, and the prickly problem of anticoagulation post-PCI in A-fib patients.

SAN DIEGO, CA—Monday’s Late-Breaking Clinical Science sessions, beginning at noon, also were a mixed bag.
UPDATE: Monday, September 24, 1:00 PM
 PREPARE-CALC was a small, 200-patient trial comparing rotational atherectomy to modified (scoring or cutting) balloons in the setting of severely calcified lesions. The trial found that rotational atherectomy was feasible in nearly all patients, with an acute success rate superior to that of the balloons (98% vs 81%, P = 0.0001).
PREPARE-CALC was a small, 200-patient trial comparing rotational atherectomy to modified (scoring or cutting) balloons in the setting of severely calcified lesions. The trial found that rotational atherectomy was feasible in nearly all patients, with an acute success rate superior to that of the balloons (98% vs 81%, P = 0.0001).
“Both approaches are equally safe and effective,” Gert Richardt, MD, PhD, said here. Use of rotational atherectomy is no longer associated with excessive late lumen loss in the era of modern drug-eluting stents, he added.
PREPARE-CALC was published simultaneously in Circulation: Cardiovascular Interventions.
*****
FAST-FFR was a prospective, multicenter trial comparing the accuracy of on-site “FFRangio” with standard pressure wire-derived FFR in 300 patients treated at 10 hospitals in the United States, Europe, and Israel. FFRangio has been developed as a potentially faster, less-cumbersome tool for physiologic testing: derived from routine coronary angiography, the technology creates a 3-D reconstruction of the coronary tree and estimates the resistance and flow across a stenosis. The technique has been tested using off-site validation; FAST FFR was conducted to test the feasibility of on-site use, with local operators blinded to pressure wire-derived FFR.
 As William Fearon, MD, showed here, the per-vessel sensitivity and specificity for FFRangio were 94% and 91%, respectively, while the diagnostic accuracy was 92%. FFRangio values correlated well with FFR measurements, and device success was 99%.
As William Fearon, MD, showed here, the per-vessel sensitivity and specificity for FFRangio were 94% and 91%, respectively, while the diagnostic accuracy was 92%. FFRangio values correlated well with FFR measurements, and device success was 99%.
“FFRangio may provide an easier and potentially faster method for performing physiology-guided assessment of the overall coronary angiogram with similar accuracy to the reference standard, coronary pressure wire-based FFR,” Fearon concluded. “This may translate into a greater percentage of patients undergoing physiologic guidance for revascularization decisions and ultimately improve long-term outcomes.”
FAST-FFR was published simultaneously in Circulation.
*****
Two long-term comparisons of coronary artery bypass surgery and drug-eluting stents for multivessel disease and left main disease capped today’s Late-Breaking Clinical Science session.
One was 10-year results from the non-randomized MAIN-COMPARE registry, which included both bare metal stents and first-generation drug-eluting stents, and was presented by Seung-Jung Park. At 10-years, rates of death and a composite endpoint of death, Q-wave MI, or stroke were no different between the PCI and the CABG groups, although target vessel failure was more common among PCI-treated patients. The second was the randomized, SYNTAX Extended Survival study (“SYNTAXES”), presented by Daniel Thuijs, MD, addressing 10-year outcomes among the nearly three-quarters of patients that have met the 10-year mark in this study. After a decade, Thuijs showed here, there was no overall survival difference between patients treated with CABG or PCI, but patients with three vessel disease, CABG appeared to provide a survival benefit. In left main disease, however, the two revascularization strategies appeared to be similar.
More soon from Michael O’Riordan.
*****
Back to the Main Arena for the third day of TCT 2018 late breakers. These hit the big screen right after the announcement of the Young Investigator Award and TCT 2018 Shark Tank winners.
Big up to Philipp Lurz, winner of the prestigious #TCT2018 Linnemeier Young Investigator Award, and special mention to finalist @lorenzo2509, trained @ICMtl ?? @TCTMD @TCTConference pic.twitter.com/XxgEmK9m2w
— Guillaume Marquis-Gravel (@G_MarquisGravel) September 24, 2018
ARIA CV wins @crfheart ‘Shark Tank Innovation Competition’!! #TCT2018 @GreggWStone @DrAsifQasim @jgranadacrf pic.twitter.com/I9379Zr4n7
— Poonam Velagapudi (@Pooh_Velagapudi) September 24, 2018
The late-breaking clinical trials that followed were a mix of intravascular imaging and anticoagulation trials.
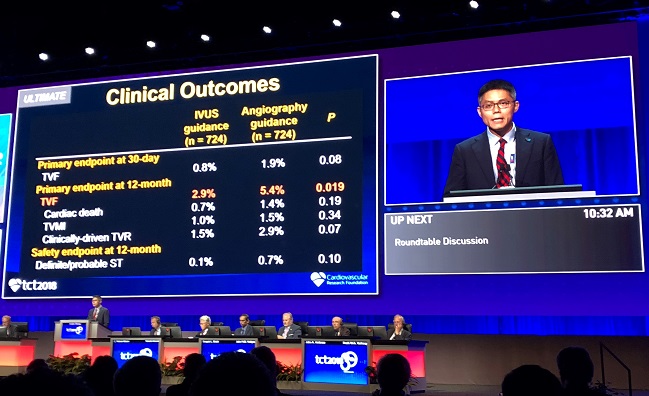 ULTIMATE, conducted at eight centers in China, was a randomized comparison of IVUS-guided DES implantation versus the eyeball test on angiography alone in an all-comers population. From August 2014 to May 2017, a total of 1,448 patients undergoing stent implantation were randomized to IVUS guidance (n = 724) or angiography guidance (n = 724). Of note, 55% of patients were found to have multivessel disease, mean lesion length was 34.5 mm, and 67% of lesions were classified as Type B2/C. As expected, IVUS-guided procedures tended to be longer and the stents used tended to be marginally longer and larger in diameter.
ULTIMATE, conducted at eight centers in China, was a randomized comparison of IVUS-guided DES implantation versus the eyeball test on angiography alone in an all-comers population. From August 2014 to May 2017, a total of 1,448 patients undergoing stent implantation were randomized to IVUS guidance (n = 724) or angiography guidance (n = 724). Of note, 55% of patients were found to have multivessel disease, mean lesion length was 34.5 mm, and 67% of lesions were classified as Type B2/C. As expected, IVUS-guided procedures tended to be longer and the stents used tended to be marginally longer and larger in diameter.
Dr. Mintz commenting on ULTIMATE study: if you don’t use ultrasound to truly optimize the results you don’t get a benefit #TCT2018
— C. Michael Gibson MD (@CMichaelGibson) September 24, 2018
At 12 months, the primary endpoint of target lesion failure was significantly reduced in the IVUS arm compared with the angiography arm: 2.9% versus 5.4% (HR 0.53; 95% CI 0.31-0.90).
In a morning press conference, presenter Jun-Jie Zhang, MD, PhD, noted that IVUS is used in approximately 80% of procedures in China. In the US, IVUS is used much more rarely, in approximately 15% of DES implantations.
Find full results here.
*****
Presenting results of the LRP study, Ron Waksman, MD, showed the feasibility and safety of using multivessel near infrared spectroscopy (NIRS) imaging to identify both vulnerable plaques and vulnerable patients who present with both stable angina and ACS.
 As Waksman showed this morning, an adjusted patient-level analysis (n = 1,271) found an 18% higher risk of experiencing nonculprit MACE event within 24 months for each 100-unit increase in maxLCBI4mm identified on NIRS. Also, the plaque-level analysis (n = 5,744) demonstrated a 45% higher risk of events within 24 months with each 100-unit increase in maxLCBI4mm in a coronary segment.
As Waksman showed this morning, an adjusted patient-level analysis (n = 1,271) found an 18% higher risk of experiencing nonculprit MACE event within 24 months for each 100-unit increase in maxLCBI4mm identified on NIRS. Also, the plaque-level analysis (n = 5,744) demonstrated a 45% higher risk of events within 24 months with each 100-unit increase in maxLCBI4mm in a coronary segment.
“Intravascular NIRS imaging in mildly or nonobstructive coronary arteries can be used as a tool to identify both patients and nonculprit arteries at high risk for future events and should be considered for use in patients undergoing cardiac catheterization with possible PCI,” Waksman said in his presentation.
Get the full story here.
*****
Despite international guidance recommending use of oral anticoagulation alone in patients with A-fib who are at least a year out from PCI, there have been no randomized trials comparing this strategy with one employing anticoagulation plus single antiplatelet therapy.
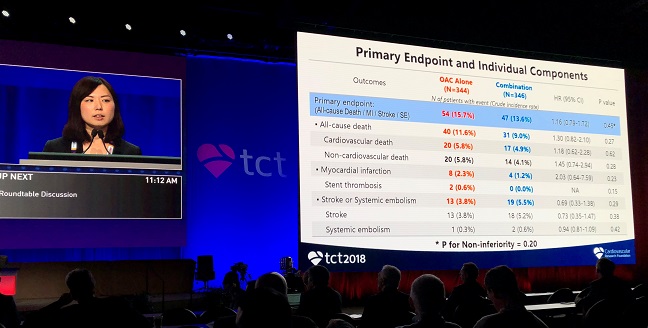 Into that void steps OAC-ALONE, a Japanese trial that enrolled 696 patients with A-fib who were more than a year out from stenting. The trial failed to establish that anticoagulation alone was noninferior to anticoagulation plus single antiplatelet therapy in terms of the primary composite endpoint of death, MI, stroke, or systemic embolism. Adding ISTH major bleeding to that endpoint to assess net clinical benefit, however, the investigators found that anticoagulation alone was noninferior, with a rate of 19.5% in that arm and 19.4% in patients receiving anticoagulation plus single antiplatelet therapy.
Into that void steps OAC-ALONE, a Japanese trial that enrolled 696 patients with A-fib who were more than a year out from stenting. The trial failed to establish that anticoagulation alone was noninferior to anticoagulation plus single antiplatelet therapy in terms of the primary composite endpoint of death, MI, stroke, or systemic embolism. Adding ISTH major bleeding to that endpoint to assess net clinical benefit, however, the investigators found that anticoagulation alone was noninferior, with a rate of 19.5% in that arm and 19.4% in patients receiving anticoagulation plus single antiplatelet therapy.
Yukiko Nakano, MD, said the primary hypothesis of the study is inconclusive because of an insufficient sample size, but concluded that anticoagulation alone might be reasonable for patients with A-fib at least a year after stenting.
Full results from OAC-ALONE are here.
*****
Shelley Wood was the Editor-in-Chief of TCTMD and the Editorial Director at the Cardiovascular Research Foundation (CRF) from October 2015…
Read Full Bio

Comments